Сейчас майские праздники и я нахожусь в деревне далеко от Москвы (>300 км). Деревня достаточно глухая, стоит в лесах и полях Калужской области, но интернет мне тут жизненно необходим для работы и он был сделан. Описание настройки 3G интернета в деревне было опубликовано на дружественном сайте 4ham.ru (статья: «Настройка 3G Интернета в глухой деревне Калужской области» ), как нибудь перенесу её и сюда.
Интернет есть, работать удаленно можно (так зачем же ехать в Москву на работу между майскими праздниками 🙂 ), но еще очень хотелось иметь офисный стационарный телефон, не люблю я софтфоны.
На складе был найден IP телефон Yealink SIP-T26P. Данный телефон удобен тем, что может быть OpenVPN клиентом.
В настройках OpenVPN клиента, есть некоторые особенности, на которые я и хочу обратить внимание в данной статье.
Настройка
Отступление
Ни какие особо хитрые или необычные настройки OpenVPN сервера я не буду описывать, похожих инструкций и более подробных полон интернет, я опишу тот минимум, который необходим для работы с телефоном Yealink.
Что имеем
Linux CentOS release 6.5 (64 bit)
cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS release 6.5 (Final) cat /proc/version Linux version 2.6.32-431.5.1.el6.x86_64 (mockbuild@c6b10.bsys.dev.centos.org) (gcc version 4.4.7 20120313 (Red Hat 4.4.7-4) (GCC) ) #1 SMP Wed Feb 12 00:41:43 UTC 2014
IP телефон Yealink SIP-T26P, Firmware Version 6.72.0.30
Настройка OpenVPN сервера
Как уже писал выше, я не буду разжёвывать процедуру настройки, акцентирую внимание только на моментах необходимых для телефона.
Установка необходимых пакетов
yum update yum install -y openvpn easy-rsa
Создание ключей и сертификатов с помощью Easy-RSA
Копируем необходимые файлы
mkdir -p /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys cp -rf /usr/share/easy-rsa/2.0/* /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/
Редактируем файл /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/vars
Образец:
# Increase this to 2048 if you # are paranoid. This will slow # down TLS negotiation performance # as well as the one-time DH parms # generation process. # Yealink поддерживает DH 1024, по умолчанию стоит 2048 export KEY_SIZE=1024 # These are the default values for fields # which will be placed in the certificate. # Don't leave any of these fields blank. export KEY_COUNTRY="RU" export KEY_PROVINCE="Moscow" export KEY_CITY="Moscow" export KEY_ORG="Trust.com" export KEY_EMAIL="support@test.local" export KEY_OU="IT"
Обратите внимание на параметр KEY_SIZE=1024, это один из тех параметров которые нужно настроить для Yealink.
Настройка конфигурационного файла OpenSSL /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/openssl-1.0.0.cnf
Yealink поддерживает Signature hash algorithm SHA1 и MD5, в OpenSSL по умолчанию SHA256, меняем параметры.
[ CA_default ] default_md= sha1 [ req ] default_md= sha1
Подготовка к созданию ключей и сертификатов
cd /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa source ./vars ./clean-all
Создание Certificate Authority, файл ca.key (он нужен и серверу и клиенту)
./build-ca
Создаём сертификат и ключ для сервера
./build-key-server server
Создаем ключ по алгоритму Diffie-Hellman
./build-dh
Создаём сертификат и ключ для клиента
./build-key yealink
Настройка конфигурационного файла OpenVPN сервера
Копируем образец конфигурационного файла
cp /usr/share/doc/openvpn-2.3.2/sample/sample-config-files/server.conf /etc/openvpn/
Пример настроек конфигурационного файла
################################################# # Sample OpenVPN 2.0 config file for # # multi-client server. # # # # This file is for the server side # # of a many-clients <-> one-server # # OpenVPN configuration. # # # # OpenVPN also supports # # single-machine <-> single-machine # # configurations (See the Examples page # # on the web site for more info). # # # # This config should work on Windows # # or Linux/BSD systems. Remember on # # Windows to quote pathnames and use # # double backslashes, e.g.: # # "C:\\Program Files\\OpenVPN\\config\\foo.key" # # # # Comments are preceded with '#' or ';' # ################################################# # Which local IP address should OpenVPN # listen on? (optional) local 10.21.0.205 # Which TCP/UDP port should OpenVPN listen on? # If you want to run multiple OpenVPN instances # on the same machine, use a different port # number for each one. You will need to # open up this port on your firewall. port 1726 # TCP or UDP server? ;proto tcp proto udp # "dev tun" will create a routed IP tunnel, # "dev tap" will create an ethernet tunnel. # Use "dev tap0" if you are ethernet bridging # and have precreated a tap0 virtual interface # and bridged it with your ethernet interface. # If you want to control access policies # over the VPN, you must create firewall # rules for the the TUN/TAP interface. # On non-Windows systems, you can give # an explicit unit number, such as tun0. # On Windows, use "dev-node" for this. # On most systems, the VPN will not function # unless you partially or fully disable # the firewall for the TUN/TAP interface. ;dev tap dev tun # Windows needs the TAP-Win32 adapter name # from the Network Connections panel if you # have more than one. On XP SP2 or higher, # you may need to selectively disable the # Windows firewall for the TAP adapter. # Non-Windows systems usually don't need this. ;dev-node MyTap # SSL/TLS root certificate (ca), certificate # (cert), and private key (key). Each client # and the server must have their own cert and # key file. The server and all clients will # use the same ca file. # # See the "easy-rsa" directory for a series # of scripts for generating RSA certificates # and private keys. Remember to use # a unique Common Name for the server # and each of the client certificates. # # Any X509 key management system can be used. # OpenVPN can also use a PKCS #12 formatted key file # (see "pkcs12" directive in man page). ca /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys/ca.crt cert /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys/server.crt key /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys/server.key # This file should be kept secret # Diffie hellman parameters. # Generate your own with: # openssl dhparam -out dh1024.pem 1024 # Substitute 2048 for 1024 if you are using # 2048 bit keys. dh /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys/dh1024.pem # Configure server mode and supply a VPN subnet # for OpenVPN to draw client addresses from. # The server will take 10.8.0.1 for itself, # the rest will be made available to clients. # Each client will be able to reach the server # on 10.8.0.1. Comment this line out if you are # ethernet bridging. See the man page for more info. server 10.21.4.0 255.255.255.0 # Maintain a record of client <-> virtual IP address # associations in this file. If OpenVPN goes down or # is restarted, reconnecting clients can be assigned # the same virtual IP address from the pool that was # previously assigned. ;ifconfig-pool-persist ipp.txt # Configure server mode for ethernet bridging. # You must first use your OS's bridging capability # to bridge the TAP interface with the ethernet # NIC interface. Then you must manually set the # IP/netmask on the bridge interface, here we # assume 10.8.0.4/255.255.255.0. Finally we # must set aside an IP range in this subnet # (start=10.8.0.50 end=10.8.0.100) to allocate # to connecting clients. Leave this line commented # out unless you are ethernet bridging. ;server-bridge 10.8.0.4 255.255.255.0 10.8.0.50 10.8.0.100 # Configure server mode for ethernet bridging # using a DHCP-proxy, where clients talk # to the OpenVPN server-side DHCP server # to receive their IP address allocation # and DNS server addresses. You must first use # your OS's bridging capability to bridge the TAP # interface with the ethernet NIC interface. # Note: this mode only works on clients (such as # Windows), where the client-side TAP adapter is # bound to a DHCP client. ;server-bridge # Push routes to the client to allow it # to reach other private subnets behind # the server. Remember that these # private subnets will also need # to know to route the OpenVPN client # address pool (10.8.0.0/255.255.255.0) # back to the OpenVPN server. push "route 10.21.0.0 255.255.240.0" ;push "route 192.168.2 255.255.255.0" # To assign specific IP addresses to specific # clients or if a connecting client has a private # subnet behind it that should also have VPN access, # use the subdirectory "ccd" for client-specific # configuration files (see man page for more info). # EXAMPLE: Suppose the client # having the certificate common name "Thelonious" # also has a small subnet behind his connecting # machine, such as 192.168.40.128/255.255.255.248. # First, uncomment out these lines: ;client-config-dir ccd ;route 192.168.40.128 255.255.255.248 # Then create a file ccd/Thelonious with this line: # iroute 192.168.40.128 255.255.255.248 # This will allow Thelonious' private subnet to # access the VPN. This example will only work # if you are routing, not bridging, i.e. you are # using "dev tun" and "server" directives. # EXAMPLE: Suppose you want to give # Thelonious a fixed VPN IP address of 10.9.0.1. # First uncomment out these lines: ;client-config-dir ccd ;route 10.9.0.0 255.255.255.252 # Then add this line to ccd/Thelonious: # ifconfig-push 10.9.0.1 10.9.0.2 # Suppose that you want to enable different # firewall access policies for different groups # of clients. There are two methods: # (1) Run multiple OpenVPN daemons, one for each # group, and firewall the TUN/TAP interface # for each group/daemon appropriately. # (2) (Advanced) Create a script to dynamically # modify the firewall in response to access # from different clients. See man # page for more info on learn-address script. ;learn-address ./script # If enabled, this directive will configure # all clients to redirect their default # network gateway through the VPN, causing # all IP traffic such as web browsing and # and DNS lookups to go through the VPN # (The OpenVPN server machine may need to NAT # or bridge the TUN/TAP interface to the internet # in order for this to work properly). ;push "redirect-gateway def1 bypass-dhcp" # Certain Windows-specific network settings # can be pushed to clients, such as DNS # or WINS server addresses. CAVEAT: # http://openvpn.net/faq.html#dhcpcaveats # The addresses below refer to the public # DNS servers provided by opendns.com. ;push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.222.222" ;push "dhcp-option DNS 208.67.220.220" # Uncomment this directive to allow different # clients to be able to "see" each other. # By default, clients will only see the server. # To force clients to only see the server, you # will also need to appropriately firewall the # server's TUN/TAP interface. client-to-client # Uncomment this directive if multiple clients # might connect with the same certificate/key # files or common names. This is recommended # only for testing purposes. For production use, # each client should have its own certificate/key # pair. # # IF YOU HAVE NOT GENERATED INDIVIDUAL # CERTIFICATE/KEY PAIRS FOR EACH CLIENT, # EACH HAVING ITS OWN UNIQUE "COMMON NAME", # UNCOMMENT THIS LINE OUT. ;duplicate-cn # The keepalive directive causes ping-like # messages to be sent back and forth over # the link so that each side knows when # the other side has gone down. # Ping every 10 seconds, assume that remote # peer is down if no ping received during # a 120 second time period. keepalive 10 120 # For extra security beyond that provided # by SSL/TLS, create an "HMAC firewall" # to help block DoS attacks and UDP port flooding. # # Generate with: # openvpn --genkey --secret ta.key # # The server and each client must have # a copy of this key. # The second parameter should be '0' # on the server and '1' on the clients. ;tls-auth ta.key 0 # This file is secret # Select a cryptographic cipher. # This config item must be copied to # the client config file as well. ;cipher BF-CBC # Blowfish (default) ;cipher AES-128-CBC # AES ;cipher DES-EDE3-CBC # Triple-DES # Enable compression on the VPN link. # If you enable it here, you must also # enable it in the client config file. comp-lzo no # The maximum number of concurrently connected # clients we want to allow. ;max-clients 100 # It's a good idea to reduce the OpenVPN # daemon's privileges after initialization. # # You can uncomment this out on # non-Windows systems. user openvpn group openvpn # The persist options will try to avoid # accessing certain resources on restart # that may no longer be accessible because # of the privilege downgrade. persist-key persist-tun # Output a short status file showing # current connections, truncated # and rewritten every minute. status /var/log/openvpn/openvpn-status.log # By default, log messages will go to the syslog (or # on Windows, if running as a service, they will go to # the "\Program Files\OpenVPN\log" directory). # Use log or log-append to override this default. # "log" will truncate the log file on OpenVPN startup, # while "log-append" will append to it. Use one # or the other (but not both). ;log /var/log/openvpn/openvpn.log log-append /var/log/openvpn/openvpn.log # Set the appropriate level of log # file verbosity. # # 0 is silent, except for fatal errors # 4 is reasonable for general usage # 5 and 6 can help to debug connection problems # 9 is extremely verbose verb 5 # Silence repeating messages. At most 20 # sequential messages of the same message # category will be output to the log. # Не записывать больше повторяющихся сообщений сразу mute 20
Если у вас, так же как и у меня, OpenVPN сервер находится за NAT/Firewall не забудьте пробросить UDP порт.
Запуск OpenVPN сервера
chkconfig openvpn on /etc/init.d/openvpn start
Настройка IP телефона Yealink для работы с OpenVPN сервером
Для телефона необходимо создать tar файл с конфигурационным файлом клиента и ключами.
Документация подробно описывающий настройку: Настройка OpenVPN в Yealink
Суть вкратце
Подготовим необходимые подкаталоги и файлы для создания tar файла
mkdir -p /etc/openvpn/client/keys cp /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys/ca.crt /etc/openvpn/client/keys cp /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys/yealink.crt /etc/openvpn/client/keys cp /etc/openvpn/easy-rsa/keys/yealink.key /etc/openvpn/client/keys
Конфигурационный файл клиента vpn.cnf
Файл кладём в /etc/openvpn/client
setenv SERVER_POLL_TIMEOUT 4 reneg-sec 604800 sndbuf 100000 rcvbuf 100000 auth-retry nointeract ############################################## # Sample client-side OpenVPN 2.0 config file # # for connecting to multi-client server. # # # # This configuration can be used by multiple # # clients, however each client should have # # its own cert and key files. # # # # On Windows, you might want to rename this # # file so it has a .ovpn extension # ############################################## # Specify that we are a client and that we # will be pulling certain config file directives # from the server. client # Use the same setting as you are using on # the server. # On most systems, the VPN will not function # unless you partially or fully disable # the firewall for the TUN/TAP interface. ;dev tap dev tun dev-type tun # Windows needs the TAP-Win32 adapter name # from the Network Connections panel # if you have more than one. On XP SP2, # you may need to disable the firewall # for the TAP adapter. ;dev-node MyTap # Are we connecting to a TCP or # UDP server? Use the same setting as # on the server. ;proto tcp ;proto udp # The hostname/IP and port of the server. # You can have multiple remote entries # to load balance between the servers. remote xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx 1726 udp ;remote my-server-2 1194 # Choose a random host from the remote # list for load-balancing. Otherwise # try hosts in the order specified. ;remote-random # Keep trying indefinitely to resolve the # host name of the OpenVPN server. Very useful # on machines which are not permanently connected # to the internet such as laptops. ;resolv-retry infinite # Most clients don't need to bind to # a specific local port number. nobind # Downgrade privileges after initialization (non-Windows only) ;user nobody ;group nobody # Try to preserve some state across restarts. ;persist-key ;persist-tun # If you are connecting through an # HTTP proxy to reach the actual OpenVPN # server, put the proxy server/IP and # port number here. See the man page # if your proxy server requires # authentication. ;http-proxy-retry # retry on connection failures ;http-proxy [proxy server] [proxy port #] # Wireless networks often produce a lot # of duplicate packets. Set this flag # to silence duplicate packet warnings. ;mute-replay-warnings # SSL/TLS parms. # See the server config file for more # description. It's best to use # a separate .crt/.key file pair # for each client. A single ca # file can be used for all clients. ca /config/openvpn/keys/ca.crt cert /config/openvpn/keys/yealink.crt key /config/openvpn/keys/yealink.key # Verify server certificate by checking # that the certicate has the nsCertType # field set to "server". This is an # important precaution to protect against # a potential attack discussed here: # http://openvpn.net/howto.html#mitm # # To use this feature, you will need to generate # your server certificates with the nsCertType # field set to "server". The build-key-server # script in the easy-rsa folder will do this. ns-cert-type server # If a tls-auth key is used on the server # then every client must also have the key. ;tls-auth ta.key 1 # Select a cryptographic cipher. # If the cipher option is used on the server # then you must also specify it here. ;cipher x # Enable compression on the VPN link. # Don't enable this unless it is also # enabled in the server config file. comp-lzo no # Set log file verbosity. verb 3 # Silence repeating messages ;mute 20
Незабываем в remote вместо xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx указать ваш адрес OpenVPN сервера.
Создание tar файла и его загрузка в телефон
cd /etc/openvpn/client tar -cvpf openvpn.tar *
Полученный openvpn.tar файл загружаем в телефон через web интерфейс.
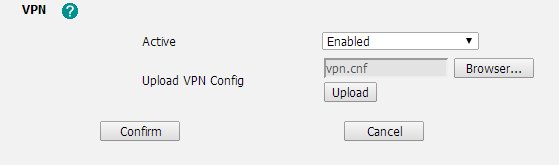
Заходим в меню Networking > Advanced, внизу будет меню «VPN», нужно поставить «Enabled» и загрузить сделанный ранее openvpn.tar файл.
У меня была проблема с доступом к меню Networking > Advanced из Firefox, открывалось просто чистое окно, я использовал Google Chrome. P.S. В версии Firmware 6.72.0.75 данная проблема не наблюдается.После перезагрузки телефона VPN должен подняться и на дисплее телефона, в правом верхнем углу должна появиться надпись «VPN».
P.S. Если вам необходимо, что бы сервер выполнял функцию маршрутизатора, незабываем включить маршрутизацию:
/sbin/sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
P.P.S. Еще раз повторюсь, данная статья не является подробным и полным описанием настройки OpenVPN сервера, это всего лишь пример настройки, который раскрывает особенности настройки OpenVPN для Yealink с которыми я столкнулся.
Похожие записи...
Latest posts by Андрей Торженов (see all)
- Куда переходить с Helpdesk OTRS? Альтернативы OTRS - 27/02/2022
- Windows 11. Не работает обновление, не входит в OneDrive, OneNote и другие Microsoft сервисы - 29/01/2022
- Попытка взлома Mikrotik? - 24/12/2021
- После обновления до Proxmox 7.1 не запускаются виртуальные машины - 28/11/2021
- libflashplayer.so пропатченный от Time bomb - 11/02/2021







Уведомление: Контроль качества соединения 3G интернет на MikroTik | 2keep.net